vue-tsc 源码解析
一、介绍
vue-tsc 是基于开源 IDE 插件 Volar 开发的针对 Vue 3 类型检查的 CLI 工具,相当于是支持 vue 文件的 tsc。其功能和用法如下:
- 类型检查:
bash
vue-tsc --noEmit- 生成类型声明文件:
bash
vue-tsc --declaration --emitDeclarationOnly二、源码分析
由于 Volar 插件近期发布了 2.0 大版本的重构,vue-tsc 源码也被重构了。下面的源码分析都是基于当前最新的 2.0.6 版本。
- language-tools/packages/tsc/index.ts
vue-tsc入口文件代码简化如下:- 调用了 volar 提供的
runTsc接口 - 然后给其传递了 3 个参数:
- 本地安装的 tsc 源码文件路径
- 文件扩展后缀配置
- 获取
vueLanguagePlugin的函数。
- 调用了 volar 提供的
- 其中,重点在于理解
runTsc和vueLanguagePlugin。
ts
// vue-tsc/index.ts
import { runTsc } from '@volar/typescript/lib/quickstart/runTsc'
import * as vue from '@vue/language-core'
import type * as ts from 'typescript'
export function run() {
let runExtensions = ['.vue']
const main = () =>
runTsc(
require.resolve('typescript/lib/tsc'),
runExtensions,
(ts, options) => {
const { configFilePath } = options.options
const vueOptions =
typeof configFilePath === 'string'
? vue.createParsedCommandLine(
ts,
ts.sys,
configFilePath.replace(windowsPathReg, '/')
).vueOptions
: {}
const resolvedVueOptions = vue.resolveVueCompilerOptions(vueOptions)
const { extensions } = resolvedVueOptions
const fakeGlobalTypesHolder = createFakeGlobalTypesHolder(options)
if (
runExtensions.length === extensions.length &&
runExtensions.every((ext) => extensions.includes(ext))
) {
const vueLanguagePlugin = vue.createVueLanguagePlugin(
ts,
(id) => id,
(fileName) => fileName === fakeGlobalTypesHolder,
options.options,
resolvedVueOptions,
false
)
return [vueLanguagePlugin]
} else {
runExtensions = extensions
throw extensionsChangedException
}
}
)
main()
}1. runTsc
- volar.js/packages/typescript/lib/quickstart/runTsc.ts
runTsc源码简化如下,runTsc是 Volar 提供的方法,目的是为了能够让 tsc 支持.vue文件,因为 tsc 默认只支持.ts,.ts,.d.ts,.js,.mts,.cts,.json等扩展文件。runTsc核心逻辑是修改 typescript 的 tsc.js 文件源码,将源码中的creatProgram方法代理成重写的方法proxyCreateProgram。然后在运行修改后的 tsc。因为- 重写
fs.readFileSync方法,在运行 tsc 命令时临时修改 tsc 源码文件,代理源码中的createProgram方法。 - 给代理后的
createProgram方法传入自定义参数,关键是第三个参数getLanguagePlugins,也就是入口文件传入的vueLanguagePlugin。
- 重写
ts
// @volar/typescript/lib/quickstart/runTsc.ts
export function runTsc(
tscPath: string,
extensions: string[],
_getLanguagePlugins: typeof getLanguagePlugins
) {
getLanguagePlugins = _getLanguagePlugins
const proxyApiPath = require.resolve('../node/proxyCreateProgram')
const readFileSync = fs.readFileSync
;(fs as any).readFileSync = (...args: any[]) => {
if (args[0] === tscPath) {
let tsc = (readFileSync as any)(...args) as string
// add allow extensions
const extsText = extensions.map((ext) => `"${ext}"`).join(', ')
tsc = replace(
tsc,
/supportedTSExtensions = .*(?=;)/,
(s) => s + `.concat([[${extsText}]])`
)
tsc = replace(
tsc,
/supportedJSExtensions = .*(?=;)/,
(s) => s + `.concat([[${extsText}]])`
)
tsc = replace(
tsc,
/allSupportedExtensions = .*(?=;)/,
(s) => s + `.concat([[${extsText}]])`
)
// proxy createProgram
tsc = replace(
tsc,
/function createProgram\(.+\) {/,
(s) =>
`var createProgram = require(${JSON.stringify(
proxyApiPath
)}).proxyCreateProgram(` +
`new Proxy({}, { get(_target, p, _receiver) { return eval(p); } } ), ` +
`_createProgram, ` +
`[${extsText}], ` +
`require(${JSON.stringify(__filename)}).getLanguagePlugins` +
`);\n` +
s.replace('createProgram', '_createProgram')
)
return tsc
}
return (readFileSync as any)(...args)
}
try {
require(tscPath)
} finally {
;(fs as any).readFileSync = readFileSync
delete require.cache[tscPath]
}
}1.1 proxyCreateProgram
- volar.js/packages/typescript/lib/node/proxyCreateProgram.ts
- 代理的
proxyCreateProgram方法简化如下。createProgram是 tsc 源码最核心方法之一,关于 tsc 源码这里先占个坑 😃
ts
// @volar/typescript/lib/node/proxyCreateProgram.ts
import type * as ts from 'typescript';
export function proxyCreateProgram(
ts: typeof import('typescript'),
original: typeof ts['createProgram'],
extensions: string[],
getLanguagePlugins: (ts: typeof import('typescript'), options: ts.CreateProgramOptions) => LanguagePlugin[],
) {
return new Proxy(original, {
apply: (target, thisArg, args) => {
const options = args[0] as ts.CreateProgramOptions;
assert(!!options.host, '!!options.host');
const sourceFileToSnapshotMap = new WeakMap<ts.SourceFile, ts.IScriptSnapshot>();
const files = createFileRegistry(..)
const originalSourceFiles = new Map<string, ts.SourceFile | undefined>();
const parsedSourceFiles = new WeakMap<ts.SourceFile, ts.SourceFile>();
const arbitraryExtensions = extensions.map(ext => `.d${ext}.ts`);
const originalHost = options.host;
options.host = { ...originalHost };
options.options.allowArbitraryExtensions = true;
options.host.getSourceFile = (..)=>{..}
options.host.resolveModuleNameLiterals = (..)=>{..}
options.host.resolveModuleNames = (..)=>{..}
const program = Reflect.apply(target, thisArg, [options]) as ts.Program;
decorateProgram(files, program);
(program as any).__volar__ = { files };
return program;
},
});
}- 其中
option.host是 tsc 内部编译文件时创建的文件读写系统(基于node:fs)。通过劫持修改host的getSourceFile,resolveModuleNameLiterals,resolveModuleNames等方法可以实现自定义的文件拦截读写逻辑。
2. createVueLanguagePlugin
- 在入口文件可以发现,
vueLanguagePlugin是通过 @vue/language-core 的接口createVueLanguagePlugin获取的。
ts
// vue-tsc/index.ts
import * as vue from '@vue/language-core'
const vueLanguagePlugin = vue.createVueLanguagePlugin(
ts,
(id) => id,
(fileName) => fileName === fakeGlobalTypesHolder,
options.options,
resolvedVueOptions,
false
)createVueLanguagePlugin定义是在 *language-tools/packages/language-core/lib/languageModule.ts。*简化代码如下所示:
ts
// @vue/language-core/lib/languageModule.ts
import { getDefaultVueLanguagePlugins } from './plugins';
import { VueGeneratedCode } from './virtualFile/vueFile';
export function createVueLanguagePlugin(
ts: typeof import('typescript'),
getFileName: (fileId: string) => string,
isValidGlobalTypesHolder: (fileName: string) => boolean,
compilerOptions: ts.CompilerOptions,
vueCompilerOptions: VueCompilerOptions,
codegenStack: boolean = false,
): LanguagePlugin<VueGeneratedCode> {
const allowLanguageIds = new Set(['vue']);
const pluginContext = {..}
const plugins = getDefaultVueLanguagePlugins(pluginContext);
return {
createVirtualCode(fileId, languageId, snapshot) {
if (allowLanguageIds.has(languageId)) {
// ..
return code;
}
},
updateVirtualCode(_fileId, code, snapshot) {
code.update(snapshot);
return code;
},
disposeVirtualCode(fileId, code, files) {
// ..
},
typescript: {
extraFileExtensions: vueCompilerOptions.extensions.map<ts.FileExtensionInfo>(ext => ({
extension: ext.slice(1),
isMixedContent: true,
scriptKind: 7 satisfies ts.ScriptKind.Deferred,
})),
getScript(rootVirtualCode) {
..
},
},
};
}- 最终返回的结果符合 Volar 中的
LanguagePlugin类型要求。
ts
// @volar/language-core/lib/types.ts
export interface VirtualCode {
id: string
languageId: string
snapshot: ts.IScriptSnapshot
mappings: CodeMapping[]
embeddedCodes?: VirtualCode[]
codegenStacks?: Stack[]
linkedCodeMappings?: Mapping[]
}
export interface LanguagePlugin<T extends VirtualCode = VirtualCode> {
createVirtualCode(
fileId: string,
languageId: string,
snapshot: ts.IScriptSnapshot,
files?: FileRegistry
): T | undefined
updateVirtualCode(
fileId: string,
virtualCode: T,
newSnapshot: ts.IScriptSnapshot,
files?: FileRegistry
): T
disposeVirtualCode?(
fileId: string,
virtualCode: T,
files?: FileRegistry
): void
typescript?: {
extraFileExtensions: ts.FileExtensionInfo[]
getScript(rootVirtualCode: T): ServiceScript | undefined
getExtraScripts?(fileName: string, rootVirtualCode: T): ExtraServiceScript[]
resolveLanguageServiceHost?(
host: ts.LanguageServiceHost
): ts.LanguageServiceHost
}
}- 其中
createVirtualCode,updateVirtualCode,disposeVirtualCode相当于VirtualCode的生命周期:创建、更新、销毁。这些方法会在上面 1.1proxyCreateProgram内部用到。 createVirtualCode方法逻辑如下:- 首次创建通过
VueGeneratedCode实例化生成 code - 使用
fileId作为 key 缓存 code 到fileRegistry - 后续针对同一个 fileId 走
code.update更新逻辑
- 首次创建通过
ts
// @vue/language-core/lib/languageModule.ts
import { VueGeneratedCode } from './virtualFile/vueFile';
..
createVirtualCode(fileId, languageId, snapshot) {
if (allowLanguageIds.has(languageId)) {
const fileName = getFileName(fileId);
if (!pluginContext.globalTypesHolder && isValidGlobalTypesHolder(fileName)) {
pluginContext.globalTypesHolder = fileName;
}
const fileRegistry = getFileRegistry(pluginContext.globalTypesHolder === fileName);
const code = fileRegistry.get(fileId);
if (code) {
code.update(snapshot);
return code;
}
else {
const code = new VueGeneratedCode(
fileName,
languageId,
snapshot,
vueCompilerOptions,
plugins,
ts,
codegenStack,
);
fileRegistry.set(fileId, code);
return code;
}
}
}- 这里两个重点是:
getFileRegistry和VueGeneratedCode
2.1 getFileRegistry
- language-tools/packages/language-core/lib/languageModule.ts
ts
// language-tools/packages/language-core/lib/languageModule.ts
function getFileRegistry(isGlobalTypesHolder: boolean) {
return getVueFileRegistry(
isGlobalTypesHolder,
getFileRegistryKey(compilerOptions, vueCompilerOptions, plugins),
vueCompilerOptions.plugins
)
}
function getVueFileRegistry(
isGlobalTypesHolder: boolean,
key: string,
plugins: VueLanguagePlugin[]
) {
const fileRegistries = isGlobalTypesHolder
? holderFileRegistries
: normalFileRegistries
let fileRegistry = fileRegistries.find(
(r) =>
r.key === key &&
r.plugins.length === plugins.length &&
r.plugins.every((plugin) => plugins.includes(plugin))
)?.files
if (!fileRegistry) {
fileRegistry = new Map()
fileRegistries.push({
key: key,
plugins: plugins,
files: fileRegistry
})
}
return fileRegistry
}
function getFileRegistryKey(
compilerOptions: ts.CompilerOptions,
vueCompilerOptions: VueCompilerOptions,
plugins: ReturnType<VueLanguagePlugin>[]
) {
const values = [
...Object.keys(vueCompilerOptions)
.sort()
.filter((key) => key !== 'plugins')
.map((key) => [key, vueCompilerOptions[key as keyof VueCompilerOptions]]),
[
...new Set(
plugins.map((plugin) => plugin.requiredCompilerOptions ?? []).flat()
)
]
.sort()
.map((key) => [key, compilerOptions[key as keyof ts.CompilerOptions]])
]
return JSON.stringify(values)
}2.2 VueGeneratedCode
- language-tools/packages/language-core/lib/virtualFile/vueFile.ts
VueGeneratedCode这个类实现了针对文件虚拟代码的“管理系统”。解析得到 vue 文件embeddedCodes的方法依赖:getEmbeddedCodes→computedFiles→computedSfc→computedVueSfc。
ts
// @volar/language-core/lib/types.d.ts
export interface VirtualCode {
id: string
languageId: string
snapshot: ts.IScriptSnapshot
mappings: CodeMapping[]
embeddedCodes?: VirtualCode[]
codegenStacks?: Stack[]
linkedCodeMappings?: Mapping[]
}
// @vue/language-core/lib/virtualFile/vueFile.ts
export class VueGeneratedCode implements VirtualCode {
// sources
id = 'main'
_snapshot: Signal<ts.IScriptSnapshot>
// computeds
getVueSfc = computedVueSfc(this.plugins, this.fileName, () =>
this._snapshot()
)
sfc = computedSfc(
this.ts,
this.plugins,
this.fileName,
() => this._snapshot(),
this.getVueSfc
)
getMappings = computedMappings(() => this._snapshot(), this.sfc)
getEmbeddedCodes = computedFiles(
this.plugins,
this.fileName,
this.sfc,
this.codegenStack
)
// others
codegenStacks: Stack[] = []
get embeddedCodes() {
return this.getEmbeddedCodes()
}
get snapshot() {
return this._snapshot()
}
get mappings() {
return this.getMappings()
}
constructor(
public fileName: string,
public languageId: string,
public initSnapshot: ts.IScriptSnapshot,
public vueCompilerOptions: VueCompilerOptions,
public plugins: ReturnType<VueLanguagePlugin>[],
public ts: typeof import('typescript'),
public codegenStack: boolean
) {
this._snapshot = signal(initSnapshot)
}
update(newSnapshot: ts.IScriptSnapshot) {
this._snapshot.set(newSnapshot)
}
}2.2.1 computedVueSfc
- language-tools/packages/language-core/lib/virtualFile/computedVueSfc.ts
- 以
computedVueSfc为例看看 computed 相关逻辑。- 首次计算,遍历传入的 plugins,调用 plugin.parseSFC 方法来解析文件。
- 如果某个插件具有
plugin.parseSFC方法,并且解析成功,则直接返回结果,并用 cache 缓存。 - 更新结果是,调用插件的
plugin.updateSFC方法并更新缓存。
ts
import type { SFCParseResult } from '@vue/compiler-sfc'
import { computed } from 'computeds'
import type * as ts from 'typescript'
import type { VueLanguagePlugin } from '../types'
export function computedVueSfc(
plugins: ReturnType<VueLanguagePlugin>[],
fileName: string,
snapshot: () => ts.IScriptSnapshot
) {
let cache:
| {
snapshot: ts.IScriptSnapshot
sfc: SFCParseResult
plugin: ReturnType<VueLanguagePlugin>
}
| undefined
return computed(() => {
// incremental update
if (cache?.plugin.updateSFC) {
const change = snapshot().getChangeRange(cache.snapshot)
if (change) {
const newSfc = cache.plugin.updateSFC(cache.sfc, {
start: change.span.start,
end: change.span.start + change.span.length,
newText: snapshot().getText(
change.span.start,
change.span.start + change.newLength
)
})
if (newSfc) {
cache.snapshot = snapshot()
// force dirty
cache.sfc = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(newSfc))
return cache.sfc
}
}
}
for (const plugin of plugins) {
const sfc = plugin.parseSFC?.(
fileName,
snapshot().getText(0, snapshot().getLength())
)
if (sfc) {
if (!sfc.errors.length) {
cache = {
snapshot: snapshot(),
sfc,
plugin
}
}
return sfc
}
}
})
}可见,核心的解析和更新功能都是依赖传入的 plugins。解析来就看看 plugins 具体逻辑。
2.3 VueLanguagePlugin
2.3.1 getDefaultVueLanguagePlugins
- language-tools/packages/language-core/lib/plugins.ts
- 追溯参数 plugins 的来源,是在
createVueLanguagePlugin中通过getDefaultVueLanguagePlugins获取得到,代码如下。- 生成 9 个默认 plugin:
useMdFilePlugin,useHtmlFilePlugin,useVueFilePlugin等等。默认的插件源码都放在 /plugins 目录下。 - 还可以通过 vue-tsc 传入额外的插件配置
vueCompilerOptions.plugins - 根据传入的插件上下文
pluginContext实例化最终的插件实例数组。
- 生成 9 个默认 plugin:
getDefaultVueLanguagePlugins在这里相当于实现了一个插件注入机制,文件的解析处理等需要定制化的逻辑交给插件内部实现,将不同文件的插件逻辑(plugins)和上述 [2.2] 中虚拟文件管理机制(VueGeneratedCode)解耦。从架构上也将 Vue 语言相关插件和 volar 服务解耦开了,正如 Volar 本身是框架无关的,特定语言相关服务应该交给 Volar 上层应用。
ts
// @vue/language-core/lib/plugins.ts
import useHtmlFilePlugin from './plugins/file-html'
import useMdFilePlugin from './plugins/file-md'
import useVueFilePlugin from './plugins/file-vue'
import useVueSfcCustomBlocks from './plugins/vue-sfc-customblocks'
import useVueSfcScriptsFormat from './plugins/vue-sfc-scripts'
import useVueSfcStyles from './plugins/vue-sfc-styles'
import useVueSfcTemplate from './plugins/vue-sfc-template'
import useHtmlTemplatePlugin from './plugins/vue-template-html'
import useVueTsx from './plugins/vue-ts'
import { pluginVersion, type VueLanguagePlugin } from './types'
export function getDefaultVueLanguagePlugins(
pluginContext: Parameters<VueLanguagePlugin>[0]
) {
const plugins: VueLanguagePlugin[] = [
useMdFilePlugin, // .md for VitePress
useHtmlFilePlugin, // .html for PetiteVue
useVueFilePlugin, // .vue and others for Vue
useHtmlTemplatePlugin,
useVueSfcStyles,
useVueSfcCustomBlocks,
useVueSfcScriptsFormat,
useVueSfcTemplate,
useVueTsx,
...pluginContext.vueCompilerOptions.plugins
]
const pluginInstances = plugins
.map((plugin) => {
try {
return plugin(pluginContext)
} catch (err) {
console.warn('[Vue] Failed to create plugin', err)
}
})
.filter((plugin): plugin is ReturnType<VueLanguagePlugin> => !!plugin)
.sort((a, b) => {
const aOrder = a.order ?? 0
const bOrder = b.order ?? 0
return aOrder - bOrder
})
return pluginInstances.filter((plugin) => {
const valid = plugin.version === pluginVersion
if (!valid) {
console.warn(
`[Vue] Plugin ${JSON.stringify(
plugin.name
)} API version incompatible, expected ${JSON.stringify(
pluginVersion
)} but got ${JSON.stringify(plugin.version)}`
)
}
return valid
})
}2.3.2 useVueFilePlugin
- 所有插件类型都是
VueLanguagePlugin,如下所示。包含一个固有属性version,和一些可选方法。不同插件包含的方法不同,功能也不同。
ts
export type VueLanguagePlugin = (ctx: {
modules: {
typescript: typeof import('typescript')
'@vue/compiler-dom': typeof import('@vue/compiler-dom')
}
compilerOptions: ts.CompilerOptions
vueCompilerOptions: VueCompilerOptions
codegenStack: boolean
globalTypesHolder: string | undefined
}) => {
version: typeof pluginVersion
name?: string
order?: number
requiredCompilerOptions?: string[]
parseSFC?(fileName: string, content: string): SFCParseResult | undefined
updateSFC?(
oldResult: SFCParseResult,
textChange: { start: number; end: number; newText: string }
): SFCParseResult | undefined
resolveTemplateCompilerOptions?(
options: CompilerDOM.CompilerOptions
): CompilerDOM.CompilerOptions
compileSFCTemplate?(
lang: string,
template: string,
options: CompilerDOM.CompilerOptions
): CompilerDOM.CodegenResult | undefined
updateSFCTemplate?(
oldResult: CompilerDOM.CodegenResult,
textChange: { start: number; end: number; newText: string }
): CompilerDOM.CodegenResult | undefined
getEmbeddedCodes?(fileName: string, sfc: Sfc): { id: string; lang: string }[]
resolveEmbeddedCode?(
fileName: string,
sfc: Sfc,
embeddedFile: VueEmbeddedCode
): void
}- 这里主要分析上面 [2.2.1] 中的
useVueFilePlugin插件,如下所示。除了固有属性version,还包含parseSFC和updateSFC方法。
ts
// @vue/language-core/lib/plugins/file-vue.ts
import type { VueLanguagePlugin } from '../types'
import { parse } from '../utils/parseSfc'
const plugin: VueLanguagePlugin = (_ctx) => {
return {
version: 2,
parseSFC(_fileName, content) {
return parse(content)
},
updateSFC(sfc, change) {
const blocks = [
sfc.descriptor.template,
sfc.descriptor.script,
sfc.descriptor.scriptSetup,
...sfc.descriptor.styles,
...sfc.descriptor.customBlocks
].filter((block): block is NonNullable<typeof block> => !!block)
const hitBlock = blocks.find(
(block) =>
change.start >= block.loc.start.offset &&
change.end <= block.loc.end.offset
)
if (!hitBlock) {
return
}
const oldContent = hitBlock.content
const newContent = (hitBlock.content =
hitBlock.content.substring(
0,
change.start - hitBlock.loc.start.offset
) +
change.newText +
hitBlock.content.substring(change.end - hitBlock.loc.start.offset))
const endTagRegex = new RegExp(`</\\s*${hitBlock.type}\\s*>`)
const insertedEndTag =
!!oldContent.match(endTagRegex) !== !!newContent.match(endTagRegex)
if (insertedEndTag) {
return
}
const lengthDiff = change.newText.length - (change.end - change.start)
for (const block of blocks) {
if (block.loc.start.offset > change.end) {
block.loc.start.offset += lengthDiff
}
if (block.loc.end.offset >= change.end) {
block.loc.end.offset += lengthDiff
}
}
return sfc
}
}
}
export default plugin2.3.3 parseSFC
- language-tools/packages/language-core/lib/utils/parseSfc.ts
parseSFC的核心逻辑是:- 解析文件源码
source得到ast:调用@vue/compiler-dom的parse方法 - 遍历一次
ast子元素,分别获取 vue sfc 文件的template,script,scriptSetup,styles以及customBlocks部分的源码和ast解析结果。
- 解析文件源码
ts
// @vue/language-core/lib/utils/parseSfc.ts
import type {
CompilerError,
SFCDescriptor,
SFCBlock,
SFCStyleBlock,
SFCScriptBlock,
SFCTemplateBlock,
SFCParseResult
} from '@vue/compiler-sfc'
import * as compiler from '@vue/compiler-dom'
export function parse(source: string): SFCParseResult {
const errors: CompilerError[] = []
// 调用 @vue/compiler-dom 的 parse 方法
const ast = compiler.parse(source, {
// there are no components at SFC parsing level
isNativeTag: () => true,
// preserve all whitespaces
isPreTag: () => true,
parseMode: 'sfc',
onError: (e) => {
errors.push(e)
},
comments: true
})
const descriptor: SFCDescriptor = {
filename: 'anonymous.vue',
source,
template: null,
script: null,
scriptSetup: null,
styles: [],
customBlocks: [],
cssVars: [],
slotted: false,
shouldForceReload: () => false
}
ast.children.forEach((node) => {
if (node.type !== compiler.NodeTypes.ELEMENT) {
return
}
switch (node.tag) {
case 'template':
descriptor.template = createBlock(node, source) as SFCTemplateBlock
break
case 'script':
const scriptBlock = createBlock(node, source) as SFCScriptBlock
const isSetup = !!scriptBlock.attrs.setup
if (isSetup && !descriptor.scriptSetup) {
descriptor.scriptSetup = scriptBlock
break
}
if (!isSetup && !descriptor.script) {
descriptor.script = scriptBlock
break
}
break
case 'style':
const styleBlock = createBlock(node, source) as SFCStyleBlock
descriptor.styles.push(styleBlock)
break
default:
descriptor.customBlocks.push(createBlock(node, source))
break
}
})
return {
descriptor,
errors
}
}三、架构图
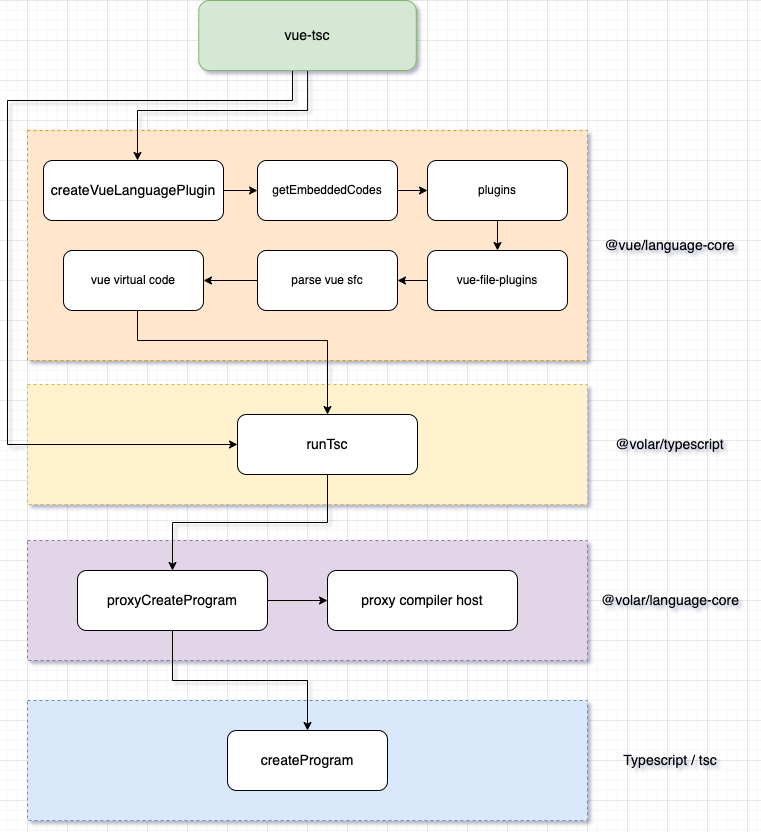
四、@mpxjs/mpx-tsc
最后加带点私货。目前我们公司团队开源的 Mpx 小程序框架也有类似 vue-tsc 的需求场景,需要在类似 .vue 的 .mpx 文件中检查 ts 代码,我们基于 vue-tsc 实现了 mpx-tsc。也欢迎感兴趣的小伙伴们参与 Mpx 开源生态。